Disorder (picking of the skin) Excoriation is a disorder characterized by recurrent skin pinching that causes skin damage. Some children with this disorder say that pinching the skin makes them feel good, but not all children do this intentionally or consciously; some don’t even remember doing it. Onset most often occurs during puberty.
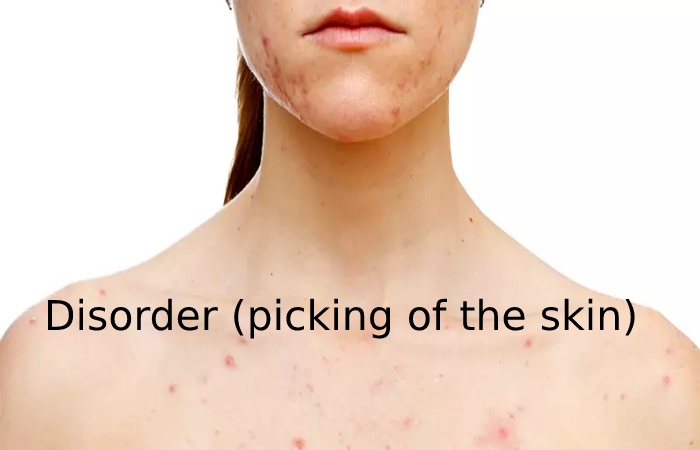
The face is the most common target for pinching the skin, but other marks can include the extremities, back, gums, lips, shoulders, scalp, stomach, chest, fingernails, and feet. A child may repeatedly pinch or “twist” a part of the body to allow the pinched part to heal.
Table of Contents
What is Excoriation Disorder?
Excoriation disorder (or picking of the skin) is a mental health problem that can constantly cause children to scratch their skin. Children with excoriation disorder picking of the skin so hard that they cause damage and pain where they are pinched. They can’t stop doing it even if they want to.
Some children bite their skin because it makes them feel good and can trigger by stress or anxiety. A lot of kids don’t even know they are doing it. Scratching the skin can cause bleeding, scabs, infections, and scarring. It can also cause embarrassment and discomfort if other people see the injury. Excoriation disorder usually begins in early adolescence.
Children with an obsessive-compulsive disorder or OCD (OCD for short) are more likely to develop excoriation disorder.
What are the Symptoms of Excoriation Disorder?
The main sign is the symbols or scabs on the child’s body from scratching or pinching the skin. Some children cross the same spot repeatedly, and others move from one point to another. Typically, children with abrasions use their fingernails to scratch, but some may use tweezers or other tools.
Children with excoriation disorder can pinch themselves anywhere on the body. But the face is the maximum common area. Children can choose from other common points: arms, legs, back, gums, lips, shoulders, scalp, stomach, chest, toenails and toenails, and cuticles.
How is Excoriation Disorder Diagnosed?
- Three things must happen for a child to be diagnosed with an excoriation disorder:
- IT have to pinch their skin so much and for so long that it causes injury.
- The must have tried to quit on their own and failed.
- Their habit must make them very uncomfortable or cause problems in their daily activities.
How is Excoriation Disorder Treated?
Usually, the pinching of the skin can stop with the help of a therapist. Cognitive-behavioral therapy or CBT (CBT for short) can help children become aware of the feelings and situations that cause them to pinch. CBT teaches children other ways to deal with feelings of pinching.
Medicines are generally not used to treat excoriation. However, some children benefit from taking antidepressants simultaneously as they are receiving treatment.
Symptoms
- Marks or scabs on the face or body.
- Try to hide or cover both the action and the resulting scabs or marks
- Spots, scabs, infections, and tissue damage
- Guilt, shame, shame
- Suffering or impairment to function meaningfully.
Processing
Treatment for excoriation usually involves psychotherapy and may include medication. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can help a child become more aware of the pinching of the skin and begin to recognize the emotions and mental states that can trigger them. Over time, with the help of a professional, you can reverse the habit. Medication is not usually the first choice for treating excoriation. However, downers such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) may prescribe while a child participates in cognitive behavioral therapy. In cognitive-behavioral therapy.
People who tend to break their skincare choose different body areas for long periods, targeting healthy and previously damaged skin. Damaged areas of the body can change over time. Frequently reported experiences that lead to scratching/pinching include
